Hydraulic Pump, Positive Displacement, and Non- Positive Displacement
Introduction
A hydraulic pump is a device that converts mechanical energy from motor to hydraulic energy like flow. We use the hydraulic pump in every single hydraulic power transmission system. It is required to be understood that a hydraulic pump never delivers the pressure but delivers the flow. The pressure is developed when the resistance to flow occurs. Hydraulic pumps are of two types i.e. Positive Displacement and Non- Positive Displacement Pumps.
Positive Displacement pumps are :
Fixed and Variable displacement pumps
Non-Positive Displacement pumps are :
Centrifugal Pump
Pump Displacement
Displacement in hydraulics refers to the flow. This means that the pump will deliver a particular amount of hydraulic fluid in Litres per minute or gallons per minute as per the pump specifications.
Types of Pumps
Classification of Pumps
Slippage and Slipping
Slipping is whenever a pump is giving less than its maximum displacement.
Slippage is the amount of liquid that could not make it to the outlet of the pump.
In positive displacement pumps, there is no chance of slippage regardless of system pressure. But there is a chance of slippage only when there are severe damages to the pump. A major disadvantage of lack of slippage is that the system pressure rises up to a certain value that can burst the pipes.
Non — Positive Displacement pumps are designed to slip. Whenever the system pressure rises to a certain limit the pump starts to slip and the pump starts to overheat. But the advantage of slippage in this system is that the system is safe from bursting as the flow of fluid will be stopped after a certain pressure limit. A non-positive displacement pump can slip makes it a good choice for any application that does not put high pressure on the pump’s outlet.
Positive Displacement Pump
A positive displacement pump is a pump in which the same amount of fluid is displaced regardless of the system pressure for every revolution of the pump shaft.
Working of Positive Displacement Pump
These types of pumps are mostly used in hydraulic systems where slippage of the hydraulic oil is not acceptable. That means these types of pumps find their usage in the system where high accuracy is required in terms of actuator motion. These types of systems are generally used in industrial applications like-
Hydraulic Presses, Hydraulic Cranes, Conveyors, etc.
In the modern world of fluid power, there is an extensive demand for such systems as these systems are highly reliable and compact in terms of power to weight ratio.
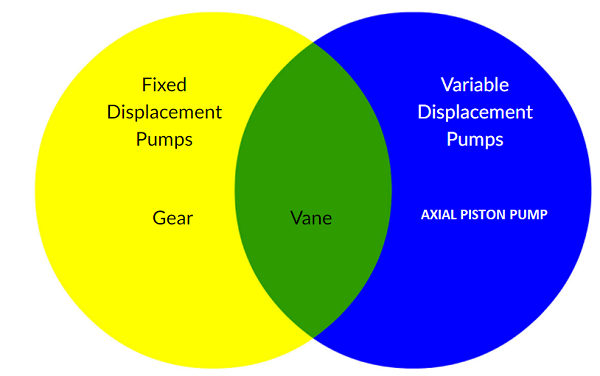
Types of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps can be classified into 2 types -
- Fixed Displacement Pump
- Variable Displacement Pump
Fixed Displacement Pump
A fixed displacement pump as the name suggests is a type of pump in which the flow of fluid can not be changed. These types of the pump do not have any mechanism to change its displacement.
Remember!
Rate of flow is a measurement of volume over time, such as liters per minute, (LPM), or gallons per minute, (GPM).
These types of pumps have the drawback that they will always displace the same amount of fluid per revolution.
If we want to change the displacement of such type of pumps there is only one way i.e. by changing the pump’s RPM by changing the speed of the prime mover.
Fixed displacement pumps are of the following types :
- Gear Pump
- Balanced Vane Pump
Variable Displacement Pump
In fixed displacement pumps we could not change the flow of the pump, on the other hand in variable displacement pumps can change flow while continuing to turn the rotor shaft at the same RPM.
Many variable displacement pumps are “reversible”, which means they can act as a hydraulic motor and convert fluid energy into mechanical energy.
Most of the variable displacement pumps have a compensator which is responsible for the change in displacement of the pump.
These types of pumps are sensitive to system pressure. Whenever the system pressure raises the compensator decreases the flow of the pump to avoid any further rise in system pressure.
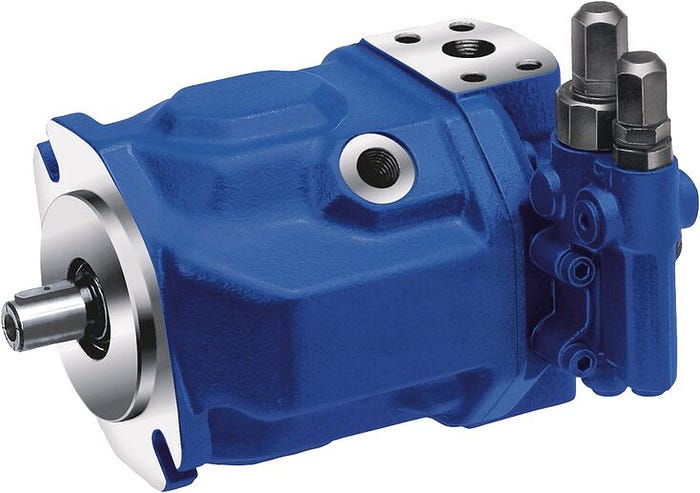

Image Credits- Bosch Rexroth (Axial Piston Pump)
Types of Variable Displacement Pumps
- Unbalanced Vane Pump
- Axial Piston Pump
Non- Positive Displacement Pump
In Non- Positive Displacement Pump the rate of flow from the pump, (GPM or LPM), changes as the restriction on the pump outlet is changed. In other words, if the pressure at the pump outlet is decreased, the flow rate will increase, and vice versa.
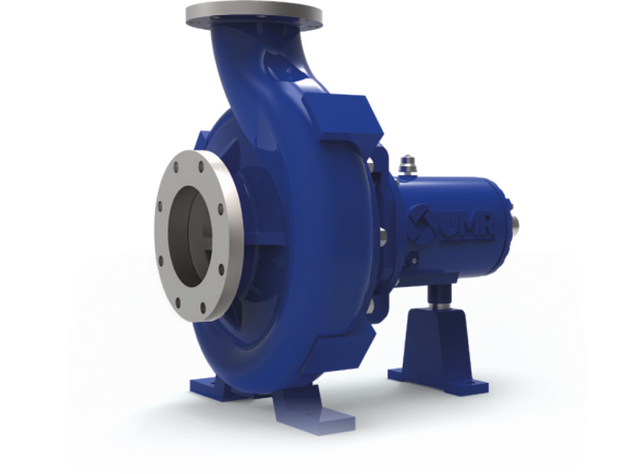

Non- Positive Displacement Pump ( Centrifugal Pump)
A Non- Positive Displacement Pump is able to adjust the flow rate according to the pressure at the outlet of the pump is because of the slippage.
The slippage is desirable in circulation pump systems because it helps the system to avoid rising the system pressure to dangerous levels and helps to save energy required by the prime mover i.e. engine or motor.
Types of Non- Positive Displacement Pumps
- Centrifugal Pumps
- Multi-Stage Pumps
- Axial (propeller) Pumps
Important Differences Between Positive and Non- Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps Non- Positive Displacement Pumps Slippage Not Desirable Desirable Working Pressure High-Pressure applications may require 700 to 800 Bars Low-pressure applications may require 15 to 20 Bars Applications Required for hydraulic motion control applications and high-pressure applications like extrusion presses Required for simple applications of transferring of the fluid-like in lubrication transfer etc. Flow is constant with change in pressure Flow changes according to rising in pressure
